Diabetes is a significant health condition that often develops slowly, with subtle signs that may go unnoticed in its early stages. Many individuals experience symptoms but attribute them to minor, unrelated issues. Understanding these early indicators is essential for timely diagnosis and effective management of the condition.
In this article, we explore nine key symptoms of diabetes or prediabetes. Recognizing these signs can empower you to take proactive steps toward better health. CONTENT IS PROVIDED FOR INFORMATIONAL PURPOSES ONLY AND IS NOT INTENDED AS A SUBSTITUTE FOR MEDICAL ADVICE. ALWAYS CONSULT YOUR DOCTOR REGARDING YOUR HEALTH AND MEDICAL CONDITIONS.
1. Darkened Patches of Skin
A velvety, darkened patch of skin on areas like the neck, armpits, groin, or other body folds could signal prediabetes. This condition, known as acanthosis nigricans, often serves as an early marker of diabetes or insulin resistance. While it may occasionally appear in individuals without health concerns, it is commonly linked to difficulties in processing insulin. If you observe such patches, schedule an appointment with your healthcare provider for a thorough evaluation.
2. Unexpected Weight Loss
You may notice weight loss despite an increased appetite or without changes to your diet or exercise routine. This occurs because the body struggles to absorb glucose from food for energy. To compensate, it breaks down stored fat and muscle, resulting in unintentional weight loss. Monitoring this symptom and discussing it with a doctor can help identify underlying blood sugar issues.
3. Vision Changes
Elevated blood sugar levels can affect the lens of the eye, leading to temporary vision problems. High glucose levels cause the lens to swell, which impairs its ability to focus, resulting in blurred or distorted vision. These changes often fluctuate with blood sugar levels. Persistent vision issues may indicate prediabetes and, if unaddressed, could increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes or long-term vision complications. Schedule an eye exam and consult your doctor if you experience these symptoms.
4. Small, Yellowish Skin Bumps
High blood sugar can elevate triglyceride levels, a type of fat in the bloodstream, potentially leading to a skin condition called eruptive xanthomatosis. In undiagnosed diabetes, small, tender bumps may appear on the skin. These bumps often have a yellowish tint on lighter skin tones or a grayish hue with a slight yellow undertone on darker skin. Commonly found on the buttocks, thighs, elbows, or knees, these itchy growths can develop anywhere on the body. Consult a healthcare professional if you notice these unusual skin changes.
5. Persistent Fatigue
Unstable blood sugar levels can lead to ongoing tiredness or exhaustion, even after sufficient rest. When insulin is not effectively utilized, the body struggles to convert glucose into energy, causing both physical and mental fatigue. This can make it difficult to stay focused or complete daily tasks. If you experience unexplained fatigue, a medical evaluation may help determine if blood sugar issues are the cause.
6. Increased Thirst and Frequent Urination
One of the earliest signs of prediabetes is excessive thirst paired with frequent trips to the bathroom. Elevated blood sugar levels prompt the kidneys to work harder to filter and remove excess glucose. When overwhelmed, the kidneys expel glucose through urine, drawing fluids from body tissues. This process leads to dehydration, triggering intense thirst. Drinking more fluids to address thirst increases urination frequency. These symptoms may become more noticeable as prediabetes progresses. Early recognition can support efforts to manage blood sugar effectively.
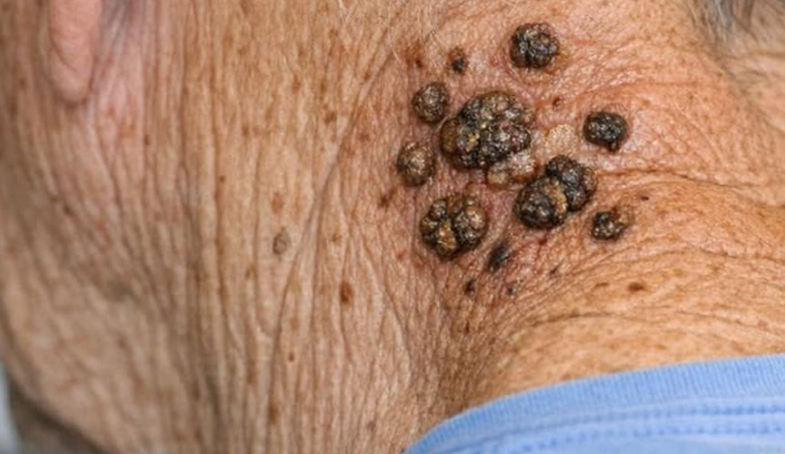
7. Skin Tags
Skin tags, or acrochordons, are small, benign growths that may appear on the skin’s surface. Some are flat, while others dangle from a thin stalk. These harmless growths often develop on the eyelids, neck, underarms, or groin. While common, an unusually high number of skin tags may suggest an underlying condition like type 2 diabetes. If you notice multiple skin tags, consult your doctor to discuss whether diabetes testing is appropriate.
8. Delayed Wound Healing
High blood sugar levels can impair the body’s ability to heal by damaging blood vessels that supply oxygen and nutrients to tissues, including the skin. Poor circulation slows the healing of cuts, bruises, or other injuries. Additionally, elevated glucose levels can weaken the immune system, increasing the risk of infections and further delaying recovery. If you notice that minor wounds take longer to heal, speak with your healthcare provider about potential blood sugar concerns.
9. Tingling or Itchy Skin
Tingling, numbness, or a burning sensation in the hands, arms, feet, or toes may indicate prediabetes. Elevated blood sugar can damage small nerves, leading to a condition called diabetic neuropathy. Some individuals describe feeling as though their socks are bunched up under their toes. Early detection of prediabetes through a blood test can help manage these symptoms and reduce the risk of developing diabetic neuropathy. Discuss testing options with your primary care provider if you experience these sensations.
Take Action for Your Health
Recognizing these symptoms early can make a significant difference in managing prediabetes or diabetes. If you observe any of these signs, consult your healthcare provider to discuss testing and appropriate next steps. Various tests, including those used to diagnose type 2 diabetes, can confirm whether prediabetes is present. Taking proactive measures can support your long-term health and well-being.
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only and does not replace professional medical advice. Always seek guidance from your doctor or a qualified healthcare professional regarding your health and medical conditions.