Soy milk is a popular alternative to cow’s milk, particularly beneficial for those with lactose intolerance. It boasts numerous nutritional benefits for all consumers.
Additionally, many people enjoy its pleasant taste, making it a preferred beverage.
In recent years, soy milk’s health impact has led to its increased popularity. Many health-conscious individuals choose it without hesitation. However, it is known by different names in various countries: “liquid” in China and “drink” in Germany. Despite its popularity, soy milk may not be as healthy as commonly believed. Research indicates that soy milk consumption can pose serious health risks.
Ingredients in soy milk include:
- Filtered water
- Whole soybeans
- Cane sugar
- Sea salt
- Carrageenan
- Natural flavor
- Calcium carbonate
- Vitamin A palmitate
- Vitamin D2
- Riboflavin
- Vitamin B12
Most of these ingredients are familiar, but carrageenan, a linear sulfated polysaccharide from red seaweeds, is worth noting. It’s used in the food industry for its stabilizing, gelling, and thickening properties.
However, carrageenan is indigestible and has no nutritional value. Despite its natural origin, it can harm the immune system, causing inflammation. Research links carrageenan to a higher risk of colon cancer and gastrointestinal issues like IBS, chronic diarrhea, and inflammatory bowel disease.
Choosing what you consume is personal, but informed decisions are crucial for health. Soy milk has long been controversial, with substantial evidence suggesting it can be harmful.
Here are ten reasons to limit or avoid soy milk:
- Soy foods are rich in aluminum, which is toxic and negatively affects the kidneys and nervous system, and is linked to Alzheimer’s disease.
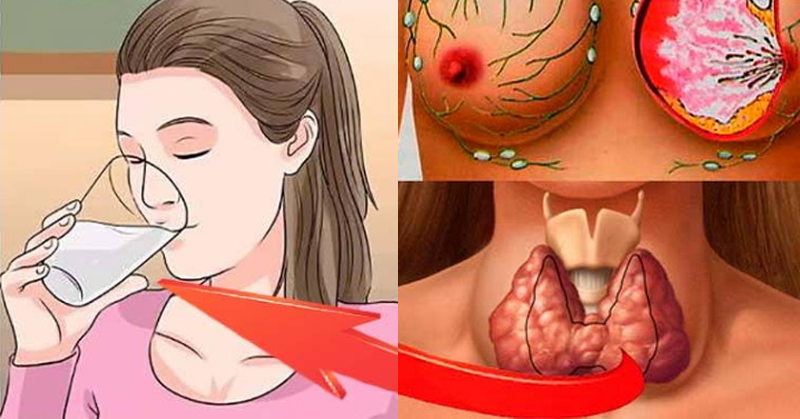
- Soy contains phytoestrogens that disrupt endocrine function, leading to infertility and ʙʀᴇᴀsᴛs cancer in women.
- Consuming two glasses of soy milk daily can significantly alter hormone levels in women, disrupting menstrual cycles.
- Toxic isoflavones in soy, such as genistein and daidzein, can promote the growth of existing ʙʀᴇᴀsᴛs cancer.
- Soy is high in phytic acid, which inhibits the absorption of zinc, copper, calcium, magnesium, and iron.
- Goitrogens in soy inhibit thyroid hormone production.
- Soybeans contain haemagglutinin, causing red blood cells to clump together.
- Nitrates, potent carcinogens, are formed during the spray-drying process.
- About 99% of soy is genetically modified, leading to high pesticide levels.
- High-temperature processing of soy protein isolate and textured vegetable protein makes the proteins difficult to digest.